Blueberries and Brain Health: Unlocking the Power of the Gut-Brain Axis
Emerging research highlights the significant role of blueberries in modulating the gut-brain axis, thereby influencing both gastrointestinal and cognitive health. The gut-brain axis is the bidirectional communication network connecting the gastrointestinal tract and the brain, involving neural, hormonal, and immunological pathways.
Blueberries and The Gut-Brain Axis
Impact on Gut Health:
Blueberries are rich in anthocyanins and other polyphenols, which possess prebiotic properties that support a healthy gut microbiome. These compounds can enhance the growth of beneficial bacteria, such as bifidobacteria, and improve intestinal barrier function. A systematic review of animal studies indicated that blueberry supplementation improved gut health by enhancing intestinal morphology, reducing gut permeability, suppressing oxidative stress, and modulating gut microbiota composition.
Influence on Cognitive Function:
The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in brain health through the production of neurotransmitters and the modulation of inflammation. By promoting a balanced gut microbiota, blueberries may indirectly support cognitive functions. For instance, a study found that daily consumption of wild blueberries led to improved executive function, better short-term memory, and faster reaction times in older adults.
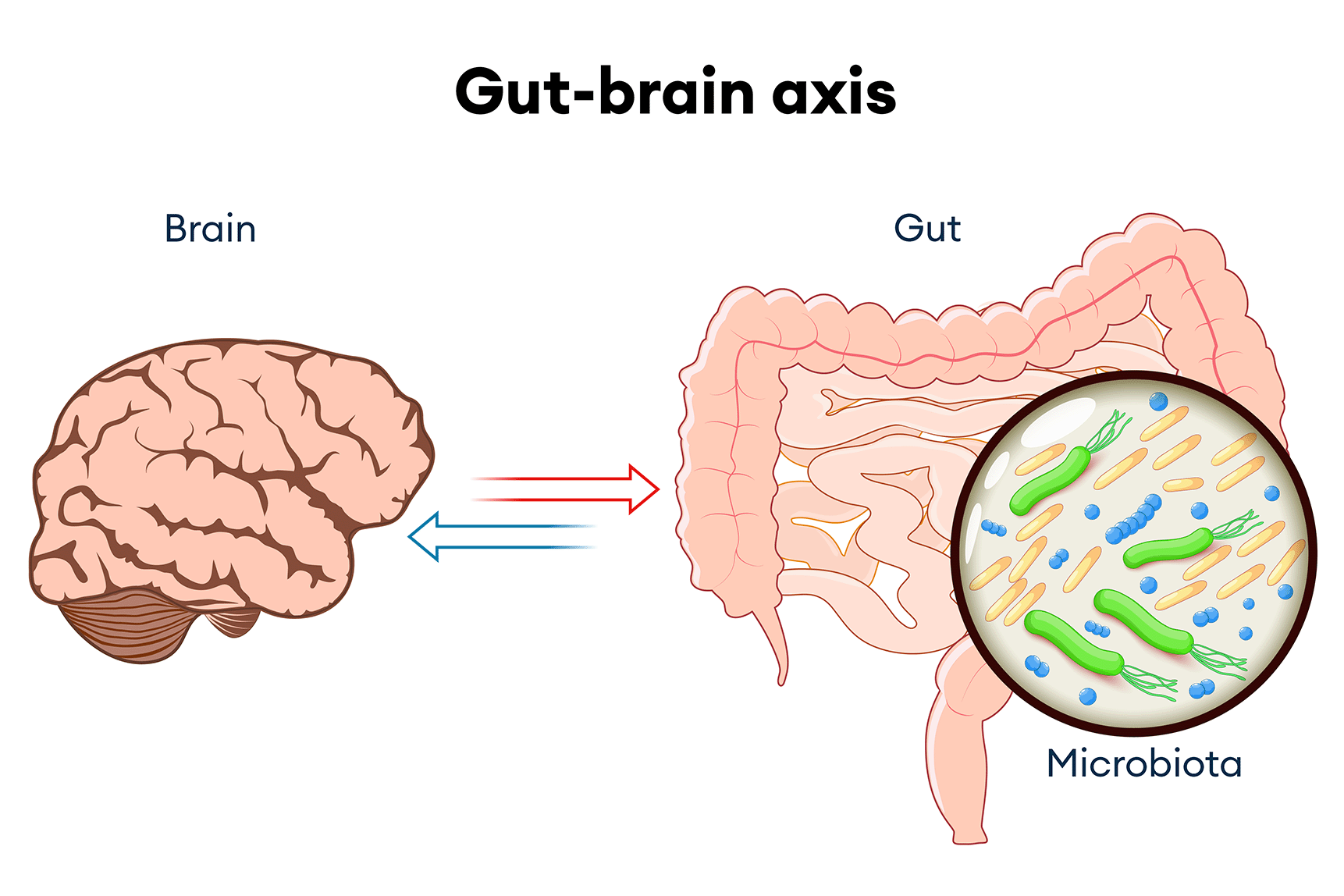
Modulation of the Gut-Brain Axis:
Research suggests that the beneficial effects of blueberries on the gut-brain axis may be mediated through several mechanisms:
Neuroinflammation Reduction:
Blueberry anthocyanins have been shown to decrease neuroinflammation, which is linked to cognitive decline. In a mouse model of autism spectrum disorder, anthocyanin-rich extracts from blueberries alleviated autism-like behaviors and reduced both neuroinflammation and gut inflammation.
Serotonin Production:
Approximately 90% of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, is produced in the gut. Blueberries may influence serotonin levels by promoting a healthy gut microbiome, positively affecting mood and cognitive functions.
Short-Chain Fatty Acid (SCFA) Production:
The fermentation of blueberry fibers by gut bacteria leads to the production of SCFAs, which have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. This process supports the integrity of the gut barrier and influences brain health.
Incorporating them into the diet may offer a natural approach to enhancing gut health and cognitive function by positively influencing the gut-brain axis.
Disclaimer
The Content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Source link
Share this article: