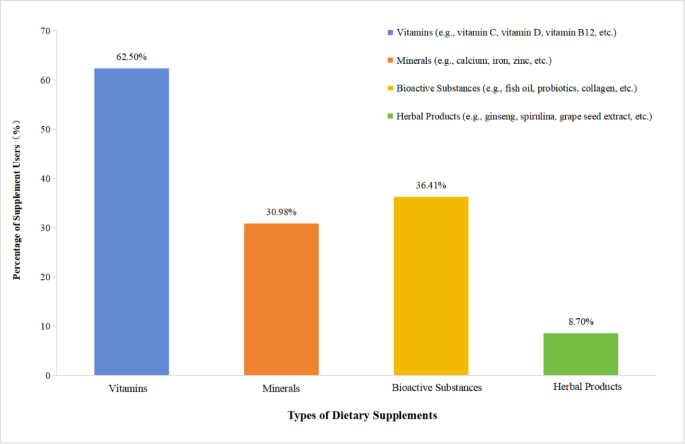
Dietary supplement consumption is associated with lower dietary quality in Chinese university students based on a cross-sectional study
Petersen, K. S. & Kris-Etherton, P. M. Diet quality assessment and the relationship between diet quality and cardiovascular disease risk. Nutrients 13, 4305 (2021).
Appel, L. J. et al. Dietary approaches to prevent and treat hypertension: a scientific statement from the American heart association. Hypertension 47, 296–308 (2006).
Fung, T. T. et al. Diet-quality scores and plasma concentrations of markers of inflammation and endothelial dysfunction. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 82, 163–173 (2005).
Krebs-Smith, S. M. et al. Update of the healthy eating index: HEI-2015. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 118, 1591–1602 (2018).
Dorrington, N., Fallaize, R., Hobbs, D., Weech, M. & Lovegrove, J. A. Diet quality index for older adults (DQI-65): development and use in predicting adherence to dietary recommendations and health markers in the UK National diet and nutrition survey. Br. J. Nutr. 128, 2193–2207 (2022).
Herforth, A. W., Wiesmann, D., Martínez-Steele, E., Andrade, G. & Monteiro, C. A. Introducing a suite of Low-Burden diet quality indicators that reflect healthy diet patterns at population level. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 4, nzaa168 (2020).
Wang, H., Herforth, A. W., Xi, B. & Zou, Z. Validation of the diet quality questionnaire in Chinese children and adolescents and relationship with pediatric overweight and obesity. Nutrients 14, 3551 (2022).
Uyar, B. T. M. et al. The DQQ is a valid tool to collect Population-Level food group consumption data: A study among women in ethiopia, vietnam, and Solomon Islands. J. Nutr. 153, 340–351 (2023).
Neri, D. et al. Ultraprocessed food consumption and dietary nutrient profiles associated with obesity: a multicountry study of children and adolescents. Obes. Rev. : Off J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 23 (Suppl 1), e13387 (2022).
Liu, J. & Mozaffarian, D. Trends in diet quality among U.S. Adults from 1999 to 2020 by race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic disadvantage. Ann. Intern. Med. 177, 841–850 (2024).
Mente, A. et al. Diet, cardiovascular disease, and mortality in 80 countries. Eur. Heart J. 44, 2560–2579 (2023).
Wang, J., Lin, X., Bloomgarden, Z. T. & Ning, G. The Jiangnan diet, a healthy diet pattern for Chinese. J. Diabetes. 12, 365–371 (2020).
Radwan, H. et al. Prevalence of dietary supplement use and associated factors among college students in the united Arab Emirates. J. Community Health. 44, 1135–1140 (2019).
Lieberman, H. R. et al. Patterns of dietary supplement use among college students. Clin. Nutr. 34, 976–985 (2015).
Sprake, E. F. et al. Dietary patterns of university students in the UK: a cross-sectional study. Nutr. J. 17, 90 (2018).
Alhazmi, A., Kuriakose, B. B., Mushfiq, S., Muzammil, K. & Hawash, M. M. Prevalence, attitudes, and practices of dietary supplements among middle-aged and older adults in Asir region, Saudi arabia: A cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 18, e0292900 (2023).
Sogari, G., Velez-Argumedo, C., Gómez, M. I. & Mora, C. College students and eating habits: A study using an ecological model for healthy behavior. Nutrients 10, 1823 (2018).
Foo, W. L., Faghy, M. A., Sparks, A., Newbury, J. W. & Gough, L. A. The effects of a nutrition education intervention on sports nutrition knowledge during a competitive season in highly trained adolescent swimmers. Nutrients 13, 2713 (2021).
Chopra, A. S. et al. The current use and evolving landscape of nutraceuticals. Pharmacol. Res. 175, 106001 (2022).
Djaoudene, O. et al. A global overview of dietary supplements: regulation, market trends, usage during the COVID-19 pandemic, and health effects. Nutrients 15, 3320 (2023).
Food supplements | EFSA. (2024). https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/topics/topic/food-supplements
Liu, Y., Guo, N., Feng, H. & Jiang, H. The prevalence of trimester-specific dietary supplements and associated factors during pregnancy: an observational study. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1135736 (2023).
Baltazar-Martins, G. et al. Prevalence and patterns of dietary supplement use in elite Spanish athletes. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 16, 30 (2019).
Chen, F. et al. Association among dietary supplement use, nutrient intake, and mortality among U.S. Adults: A cohort study. Ann. Intern. Med. 170, 604–613 (2019).
Mudnić, Ž. et al. Assessment of nutrient intake and diet quality in adolescent dietary supplement users vs. Non-Users: the CRO-PALS longitudinal study. Nutrients 15, 2783 (2023).
Pouchieu, C. et al. Sociodemographic, lifestyle and dietary correlates of dietary supplement use in a large sample of French adults: results from the NutriNet-Santé cohort study. Br. J. Nutr. 110, 1480–1491 (2013).
Albasheer, O. et al. Utilisation of the health belief model to study the behavioural intentions relating to obesity management among university students: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 14, e079783 (2024).
Liu, H. et al. Investigation and comparison of nutritional supplement use, knowledge, and attitudes in medical and non-medical students in China. Nutrients 10, 1810 (2018).
Gallè, F. et al. Assessment of dietary supplement consumption among Italian university students: the multicenter disco study. Nutr. (burbank Angeles Cty. Calif). 107, 111902 (2023).
Huang, L., Yoo, H. J., Abe, S. & Yoon, J. Dietary supplement use and its related factors among Chinese international and Korean college students in South Korea. Nutr. Res. Pract. 17, 341–355 (2023).
Owens, D. J. et al. Efficacy of High-Dose vitamin D supplements for elite athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 49, 349–356 (2017).
Wang-Chen, Y., Kellow, N. J. & Choi, T. S. T. Exploring the determinants of food choice in Chinese immigrants living in Australia and Chinese people living in Mainland china: a qualitative study. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. : Off J. Br. Diet. Assoc. 36, 1576–1588 (2023).
Hou, Y. & Jiang, J. G. Origin and concept of medicine food homology and its application in modern functional foods. Food Funct. 4, 1727–1741 (2013).
Xie, X. et al. Associations of diet quality and daily free sugar intake with depressive and anxiety symptoms among Chinese adolescents. J. Affect. Disord. 350, 550–558 (2024).
Miskeen, E. et al. Factors influencing family planning decisions in Saudi Arabia. BMC Women’s Health. 25, 222 (2025).
Chen, C., Lu, F. C. & Department of Disease Control Ministry of Health, PR China. The guidelines for prevention and control of overweight and obesity in Chinese adults. Biomed. Environ. Sci. : BES. 17 (Suppl), 1–36 (2004).
Iłowiecka, K. et al. Eating habits, and health behaviors among dietary supplement users in three European countries. Front. Public. Health. 10, 892233 (2022). Lifestyle.
Dietary supplement fact sheets. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/list-all/
Nguyen, P. H., Neupane, S., Pant, A., Avula, R. & Herforth, A. Diet quality among mothers and children in india: roles of social and behavior change communication and Nutrition-Sensitive social protection programs. J. Nutr. 154, 2784–2794 (2024).
Healthy diet. https://www.who.int/china/health-topics/healthy-diet
Popkin, B. M. & Ng, S. W. The nutrition transition to a stage of high obesity and noncommunicable disease prevalence dominated by ultra-processed foods is not inevitable. Obes. Rev. : Off J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 23, e13366 (2022).
Zhao, R. et al. Geographic variations in dietary patterns and their associations with overweight/obesity and hypertension in china: findings from China nutrition and health surveillance (2015–2017). Nutrients 14, 3949 (2022).
Sicinska, E., Madej, D., Szmidt, M. K., Januszko, O. & Kaluza, J. Dietary supplement use in relation to Socio-Demographic and lifestyle factors, including adherence to Mediterranean-Style diet in university students. Nutrients 14, 2745 (2022).
El Khoury, D., Hansen, J., Tabakos, M., Spriet, L. L. & Brauer, P. Dietary supplement use among Non-athlete students at a Canadian university: A Pilot-Survey. Nutrients 12, 2284 (2020).
Vidović, B., Đuričić, B., Odalović, M., Milošević Georgiev, A. & Tadić, I. Dietary supplements use among Serbian undergraduate students of different academic fields. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health. 19, 11036 (2022).
Barnes, K., Ball, L., Desbrow, B., Alsharairi, N. & Ahmed, F. Consumption and reasons for use of dietary supplements in an Australian university population. Nutrition 32, 524–530 (2016).
Nakhal, S. A., Domiati, S. A., Amin, M. E. K. & El-Lakany, A. M. Assessment of pharmacy students’ knowledge, attitude, and practice toward herbal dietary supplements. J. Am. Coll. Health: J. ACH. 70, 1826–1830 (2022).
Elsahoryi, N. A. et al. Prevalence of dietary supplement use and knowledge, attitudes, practice (KAP) and associated factors in student population: A cross-sectional study. Heliyon 9, e14736 (2023).
Wiltgren, A. R. et al. Micronutrient supplement use and diet quality in university students. Nutrients 7, 1094–1107 (2015).
Ishitsuka, K., Asakura, K. & Sasaki, S. Food and nutrient intake in dietary supplement users: a nationwide school-based study in Japan. J. Nutr. Sci. 11, e29 (2022).
Kim, H., Hu, E. A. & Rebholz, C. M. Ultra-processed food intake and mortality in the USA: results from the third National health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES III, 1988–1994). Public. Health Nutr. 22, 1777–1785 (2019).
Bangasser, D. A. & Cuarenta, A. Sex differences in anxiety and depression: circuits and mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 22, 674–684 (2021).
Wu, J. et al. Dietary knowledge, attitude, practice survey and nutritional knowledge-based intervention: a cross-sectional and randomized controlled trial study among college undergraduates in China. Nutrients 16, 2365 (2024).
Hartman, T. J. et al. Self-reported dietary supplement use is reproducible and relatively valid in the cancer prevention study-3 diet assessment substudy. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 122, 1665–1676e2 (2022).
Source link
Share this article: